library(sf)
library(tidyverse)
library(leaflet)
library(htmltools)
This is a walk-through tutorial to get from MetaWards output to a map plot (choropleth). The code presented here can be used to write custom functions for easy plotting of model output.
Note: This section is only for completeness, to run the code simply jump to the next section.
The 2011 census ward boundaries shapefile were be downloaded from
statistics.digitalresources.jisc.ac.uk.
I used the mapshaper command line tool (see https://github.com/mbloch/mapshaper) to reduce the number of points and thus bring the filesize down from 350Mb to about 3Mb. The mapshaper shell commands used were
mapshaper infuse_ward_lyr_2011.shp -simplify visvalingam 0.005 \
-o force infuse_ward_lyr_2011_coarse.shp
mapshaper infuse_ward_lyr_2011_coarse.shp snap snap-interval=100 \
-o force infuse_ward_lyr_2011_coarse.shp
Then I transformed the spatial polygons data frame to a sf object in the proper projection and saved it for later use:
library(rgdal)
wards_sf = readOGR('infuse_ward_lyr_2011', 'infuse_ward_lyr_2011_coarse') %>%
st_as_sf() %>%
st_cast('MULTIPOLYGON') %>%
st_transform('+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs') %>%
rename(WD11CD = geo_code)
save(file='wards_sf.Rdata', list='wards_sf')
Download link: wards_sf.Rdata
load('wards_sf.Rdata')
An interactive map of the raw wards boundary data can be displayed in the browser with
# not run:
leaflet(wards_sf) %>%
addTiles() %>%
addPolygons(col='black', weight=1)
Next we load a MetaWards model output. Here we use the file
wards_trajectory_I.csv.bz2 from the 0i3v0i0x001 run in the
experiment
here.
The outputs in this experiment are timeseries of number of infections for each
ward. We extract only the day and ward* columns and calculate the maximum
number of infections per ward:
# load metawards output
mw_output = read.csv('wards_trajectory_I.csv.bz2')
# transform to tbl and calculate max. number of infections per ward
max_infect =
mw_output %>%
as_tibble %>%
select(day, starts_with('ward')) %>%
gather('ward', 'infect', -day) %>%
group_by(ward) %>%
summarise(max_infect = max(infect))
Next we remove ward[0] and extract the integer index of each ward so we can
later match them with the ward ID from the MetaWards lookup table.
# remove ward 0, extract ward index from col name, and match with ward id
max_infect_ward =
max_infect %>%
filter(ward != 'ward.0.') %>%
mutate(FID = as.numeric(str_extract(ward, '\\d+')))
The MetaWards ward lookup table Ward_Lookup.csv was downloaded from
here.
The first column holds the ward id (WD11CD) which we extract and join it with
maximum infections data frame on column name FID. The WD11CD is also a column
in the wards boundaries data so it will be used to combine the data frames
later.
metawards_lookup = read.csv('Ward_Lookup.csv') %>%
as_tibble %>%
select(WD11CD, FID)
max_infect_ward = left_join(max_infect_ward, metawards_lookup, by='FID')
TODO: chase this up later, but ok for now
setdiff(metawards_lookup$WD11CD, wards_sf$WD11CD)
## [1] "E05003230" "E05003216" "W05000053" "W05000055" "W05000058" "W05000068"
## [7] "W05000080" "W05000081" "W05000082" "W05000083" "W05000084" "W05000088"
## [13] "W05000294" "W05000300" "W05000309" "W05000001" "W05000108" "W05000035"
## [19] "W05000041" "W05000045" "W05000047" "W05000050" "W05000320" "W05000604"
## [25] "W05000954" "W05000958" "W05000896" "E05006972" "E05006554" "E05006566"
## [31] "E05000002" "E05000003" "E05000004" "E05000005" "E05000006" "E05000007"
## [37] "E05000008" "E05000009" "E05000010" "E05000011" "E05000012" "E05000013"
## [43] "E05000014" "E05000016" "E05000017" "E05000018" "E05000019" "E05000020"
## [49] "E05000021" "E05000022" "E05000023" "E05000024" "E05000025" "E05006982"
## [55] "E05008322" "E05008323" "E05008324" "E05008325" "E05008326" "E05005228"
## [61] "E05005246"
Now matching infection data from the model run to the ward boundaries is a
simple merge by WD11CD:
# merge data frames
max_infect_df = merge(wards_sf, max_infect_ward, by='WD11CD')
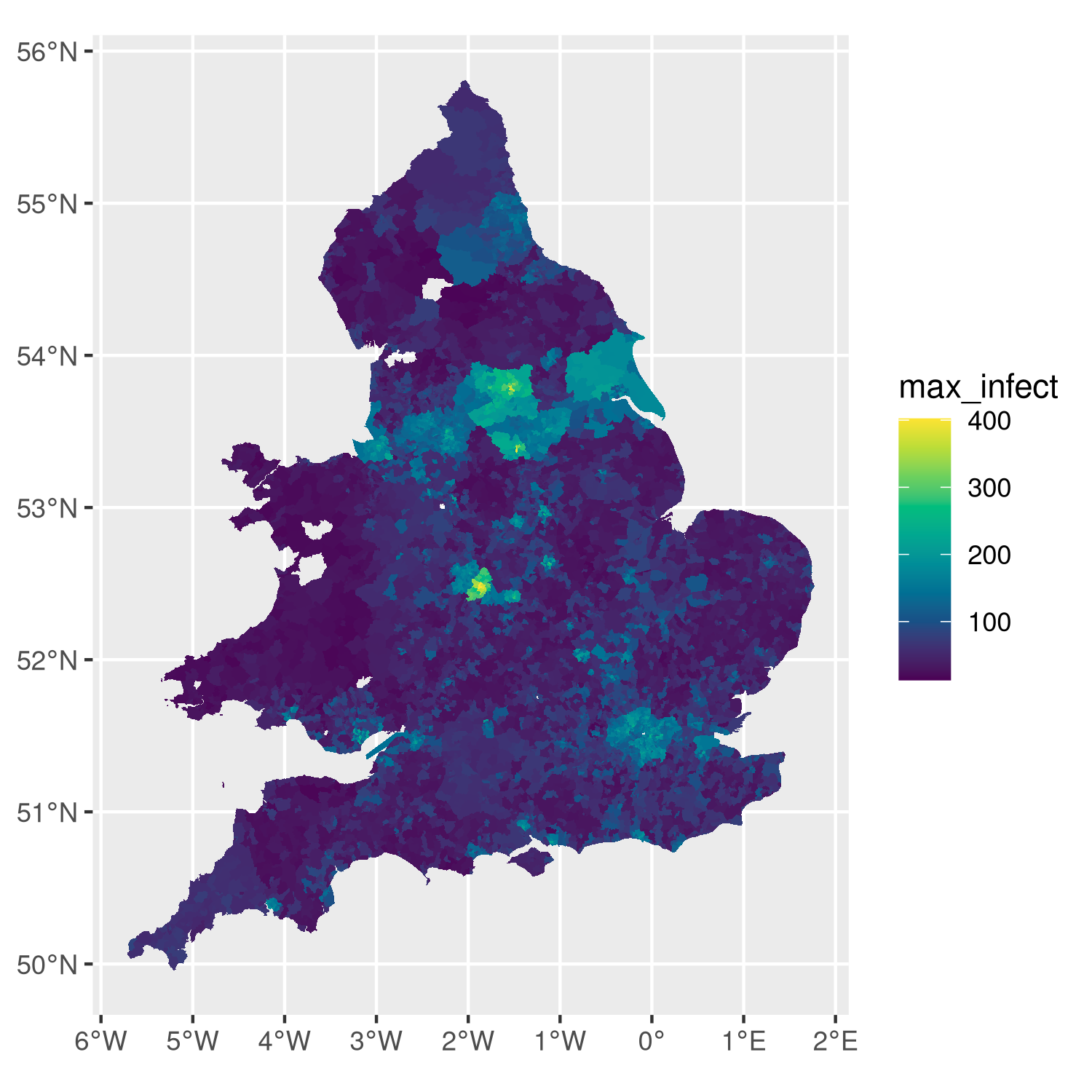
# ggplot object (13Mb)
plt = ggplot(max_infect_df) +
geom_sf(aes(fill=max_infect), lwd=0) +
scale_fill_gradientn(colours=hcl.colors(n=10))
# show
plt

# to save:
# ggsave('plot.png', plt)
To produce a cool interactive, zoomable map with hover effect, use
leaflet:
# not run:
palette = colorNumeric(palette="viridis", domain=max_infect_df$max_infect)
max_infect_df = max_infect_df %>%
mutate(text = paste(name, max_infect, sep=': '))
map = leaflet(max_infect_df) %>%
addTiles() %>%
addPolygons(fillColor=~palette(max_infect), fillOpacity=0.9,
col='black', weight=2, label = ~htmlEscape(text)) %>%
addLegend(pal=palette, values=~max_infect, opacity=1,
title='Maximum no\n of infections')
# to show map in browser do
# print(map)
# save as html widget
htmlwidgets::saveWidget(map, file='metawards_output_map.html')